PIM System Definition
A Product Information Management (PIM) system is a centralized software platform that enables businesses to collect, manage, enrich, and distribute product information across multiple sales channels. PIM systems serve as the single source of truth for all product data, ensuring consistency and accuracy across websites, marketplaces, catalogs, and other customer touchpoints.
Think of a PIM system as a digital hub where all your product information lives - from basic details like names and descriptions to complex technical specifications, images, videos, pricing, and marketing content. Instead of managing product data in spreadsheets or across multiple disconnected systems, PIM centralizes everything in one organized, accessible platform.
Core Functions of PIM Systems
Data Collection and Import
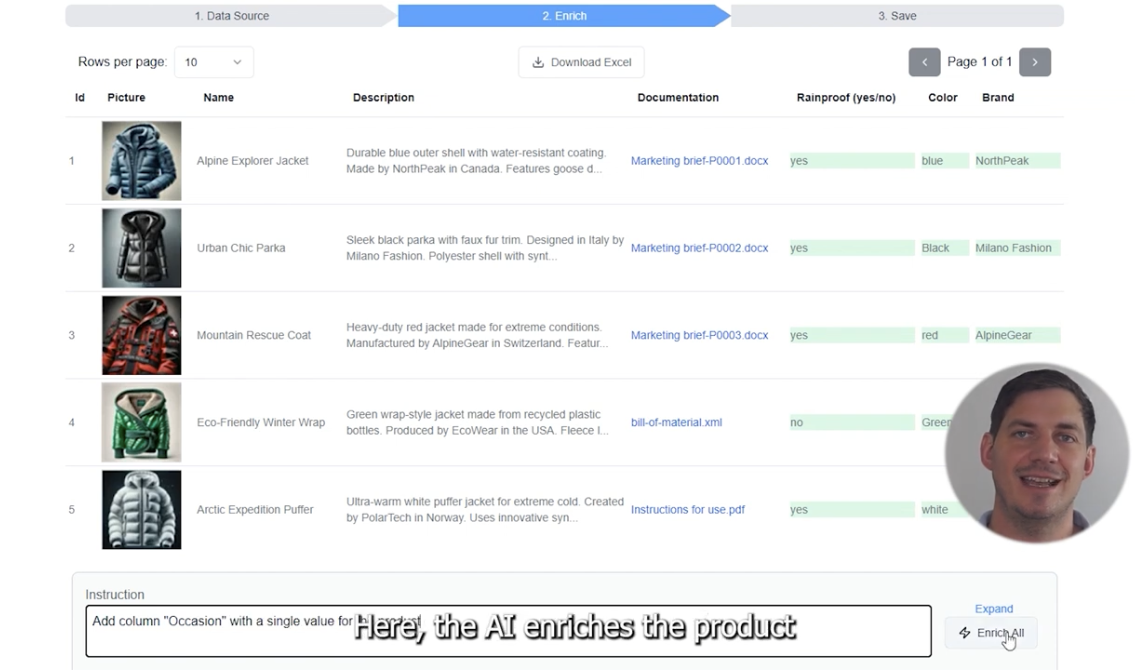
PIM systems gather product information from various sources including suppliers, manufacturers, internal teams, and external databases. Modern PIMs support automated imports from ERP systems, supplier feeds, and bulk uploads via Excel or CSV files.
Data Enrichment and Quality
Beyond basic storage, PIMs provide tools for enriching product data with descriptions, specifications, images, videos, and marketing content. Built-in validation rules ensure data quality and completeness before publication.
Workflow and Collaboration
Team collaboration features enable multiple users to work on product data simultaneously, with approval workflows ensuring quality control. Users can be assigned specific products or categories, with notifications tracking progress and deadlines.
Multi-Channel Distribution
PIMs syndicate product information to various channels including e-commerce websites, marketplaces (Amazon, eBay), print catalogs, mobile apps, and retail systems. Channel-specific formatting ensures data appears correctly across different platforms.
Different PIM systems organize product data using various approaches, each with distinct advantages for different business needs
| Entity | Vendor Name | Description | Key Attributes | Relationships |
|---|---|---|---|---|
Product-Centric Model | Traditional PIM Approach | Products are the primary entity with variants, categories, and assets as supporting elements | product records variant relationships category assignments | products have variants products belong to categories products link to assets |
Entity-Agnostic Model | Flexible MDM Approach | Any business object can be modeled with equal capabilities - products, suppliers, customers | configurable entities custom relationships flexible attributes | any entity to any entity hierarchical structures cross-domain connections |
Family-Based Model | Template-Driven Approach | Product families define attribute templates that products inherit, ensuring consistency | family definitions inherited attributes variant rules | products belong to families families define structure variants inherit from families |
JSON Schema Model | Flexible Document Approach | Products stored as flexible JSON documents with dynamic schema capabilities | document structure schema flexibility nested attributes | document references embedded relationships dynamic connections |
"A PIM system is fundamentally about creating a single source of truth for product information. The best PIMs don't just store data - they enable teams to collaborate, maintain quality, and distribute information efficiently across all channels."
Key Benefits of PIM Systems
Centralized Data Management
Eliminate data silos by consolidating product information from multiple sources into one authoritative system. This reduces errors, saves time, and ensures everyone works with the same accurate data.
Improved Data Quality
Built-in validation rules, completeness scoring, and approval workflows ensure product data meets quality standards before publication. Automated checks catch errors that manual processes often miss.
Faster Time-to-Market
Streamlined workflows and automated syndication capabilities enable faster product launches. Teams can collaborate efficiently, and new products reach multiple channels simultaneously rather than sequentially.
Enhanced Customer Experience
Consistent, accurate product information across all touchpoints improves customer confidence and reduces returns. Rich content with high-quality images and detailed specifications helps customers make informed decisions.
Operational Efficiency
Reduce manual work through automation, bulk operations, and workflow management. Teams can focus on strategic activities rather than repetitive data entry and formatting tasks.
Scalability and Growth
PIM systems scale with business growth, supporting increasing product volumes, new channels, and international expansion without proportional increases in management overhead.
Standard attribute types found across most PIM systems for storing different kinds of product information
| Common Name | Vendor Name | Description | Operators | Examples |
|---|---|---|---|---|
Text | String, Text, Textarea | Basic text fields for names, descriptions, and short content | Equals Contains Starts With Is Empty | Product name Short description SKU code |
Rich Text | HTML, WYSIWYG, Rich Text | Formatted text with styling, links, and embedded content | Contains Is Empty | Product description Marketing copy Usage instructions |
Number | Integer, Decimal, Numeric | Numeric values for measurements, quantities, and calculations | Equals Greater Than Less Than Between | Weight Dimensions Quantity in stock |
Currency | Price, Currency, Money | Monetary values with currency support and formatting | Equals Greater Than Less Than Between | Price MSRP Cost |
Date | Date, DateTime, Timestamp | Date and time values for scheduling and tracking | Equals Before After Between | Launch date Last updated Expiry date |
Boolean | Boolean, Checkbox, Yes/No | True/false values for binary properties | Is True Is False | Is active Featured product Requires shipping |
Single Select | Dropdown, List, Option | Single choice from predefined options | Equals In List Not In List | Brand Category Status |
Multi Select | Multi-select, Tags, Array | Multiple choices from predefined options | Contains Any Contains All Is Empty | Features Materials Compatible products |
Asset Reference | Image, File, Media, Asset | Links to digital assets like images, videos, and documents | Has Asset Is Empty | Product images Videos Manuals and documentation |
Entity Reference | Relation, Link, Reference | References to other products or entities in the system | Equals In List Is Empty | Related products Accessories Replacement parts |
Who Needs a PIM System?
E-commerce and Retail Businesses
Companies selling online through multiple channels benefit significantly from PIM systems. Whether you're managing hundreds or thousands of products across your website, Amazon, eBay, and other marketplaces, PIM ensures consistency and reduces manual work.
Manufacturers and Distributors
Businesses that create or distribute products need PIM to manage technical specifications, compliance data, and product relationships. PIM systems help organize complex product hierarchies and support B2B sales processes.
Multi-Channel Retailers
Organizations selling through physical stores, online platforms, mobile apps, and catalogs need centralized product data management. PIM enables consistent product presentation across all touchpoints.
International Businesses
Companies operating in multiple countries require localized product information in different languages and currencies. PIM systems provide built-in localization capabilities and regional compliance support.
Growing Product Catalogs
When managing product information in spreadsheets becomes unwieldy (typically 500+ products), PIM systems provide the structure and automation needed for efficient scaling.
"The decision to implement a PIM system usually comes when spreadsheets and manual processes can no longer keep up with business growth. The key is choosing a system that matches your data complexity and channel requirements."
PIM vs. Alternative Solutions
PIM vs. Spreadsheets
While Excel or Google Sheets work for small product catalogs, they lack collaboration features, version control, and automation capabilities. PIM systems provide structured data management, user permissions, and automated workflows that spreadsheets cannot match.
PIM vs. E-commerce Platforms
E-commerce platforms like Shopify or Magento include basic product management, but they're designed for single-channel use. PIM systems excel at multi-channel distribution and complex product data relationships.
PIM vs. ERP Systems
ERP systems manage transactional data (orders, inventory, accounting) but aren't optimized for marketing content and multi-channel syndication. PIM complements ERP by focusing on product information rather than transactions.
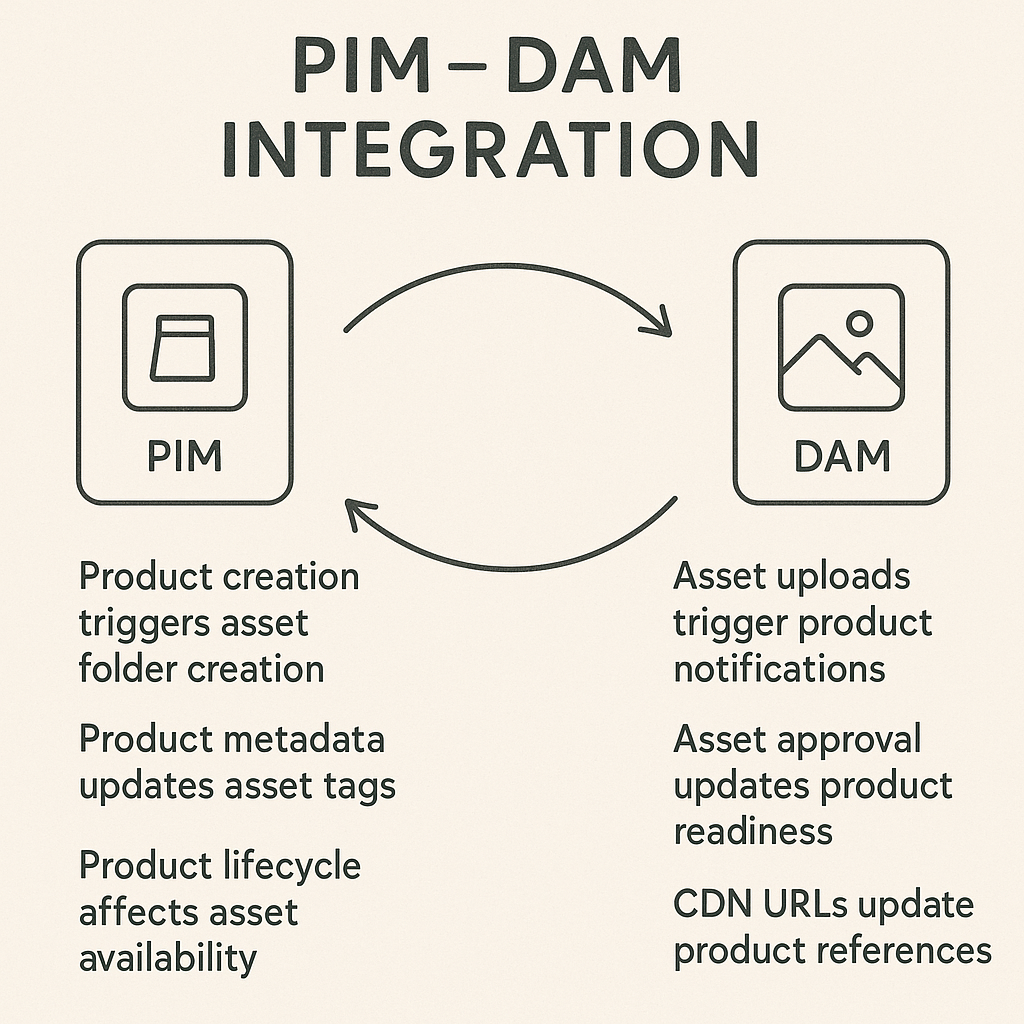
PIM vs. DAM Systems
Digital Asset Management (DAM) systems store and organize media files but lack product data structure. Many organizations use both PIM and DAM together, or choose PIM systems with built-in DAM capabilities.
PIM and DAM Integration
Many businesses need both product data management and digital asset management. Learn about the technical approaches for integrating PIM and DAM systems effectively.
Read Integration GuideHow to Choose the Right PIM System
Assess Your Data Complexity
Consider the complexity of your product data model. Simple catalogs work well with basic PIM systems, while complex B2B scenarios with custom entities may require more flexible platforms.
Evaluate Channel Requirements
List all the channels where you sell products and their specific data requirements. Some PIM systems excel at marketplace syndication, while others focus on enterprise workflows.
Consider Team Collaboration Needs
Evaluate how many people will work with product data and their roles. Some PIMs emphasize user-friendly interfaces, while others prioritize advanced workflow capabilities.
Plan for Growth
Choose a system that can scale with your business. Consider future product volumes, new channels, and international expansion requirements.
Integration Requirements
Assess how the PIM will integrate with existing systems like ERP, e-commerce platforms, and marketing tools. API quality and pre-built connectors are important factors.
Discover how AI is transforming PIM systems with automated content generation, intelligent syndication, and enhanced productivity.
Explore detailed reviews of PIM platforms to understand their unique approaches and capabilities
PIM Implementation Considerations
Data Migration Planning
Plan how to migrate existing product data from spreadsheets, legacy systems, or multiple databases. Most PIM implementations require data cleaning and standardization before migration.
Team Training and Adoption
Successful PIM implementation requires user adoption across multiple teams. Plan for training programs and change management to ensure teams embrace the new system.
Workflow Design
Design approval workflows and user permissions that match your business processes. Consider how products move from creation through enrichment to publication.
Integration Timeline
Plan integrations with existing systems including ERP, e-commerce platforms, and marketing tools. API development and testing require adequate time allocation.
Content Strategy
Develop standards for product content including image specifications, description formats, and attribute naming conventions. Consistency improves data quality and user experience.
Essential strategic and technical considerations for PIM planning and implementation
"Modern PIM systems are evolving beyond data storage to include AI-powered content generation, automated syndication, and intelligent workflow optimization. The future of PIM is about augmenting human capabilities, not replacing them."
Getting Started with PIM
PIM systems transform how businesses manage product information, providing the foundation for efficient multi-channel commerce and superior customer experiences. While the choice between different PIM platforms depends on specific business requirements, the core benefits - centralized data management, improved quality, and operational efficiency - apply universally.
The key to successful PIM implementation lies in understanding your current challenges, defining clear objectives, and choosing a platform that aligns with your data complexity and channel requirements. Whether you're managing hundreds or thousands of products, selling through multiple channels, or expanding internationally, PIM systems provide the structure and automation needed to scale efficiently.
As PIM technology continues evolving with AI-powered features and enhanced automation capabilities, early adoption of these technologies can provide significant competitive advantages in the rapidly changing digital commerce landscape.
Ready to Choose a PIM System?
Compare leading PIM platforms with detailed technical analysis, data model comparisons, and real-world implementation insights.
Compare PIM Systems